Carbon Capture Technology: The Future of Climate Change Mitigation
As the world grapples with the escalating crisis of climate change, one technology has emerged as a beacon of hope: Carbon Capture Technology.
This innovative solution, which involves capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from various sources and either storing it underground or repurposing it, is being hailed as a game-changer in our fight against global warming.
The Science of Carbon Capture
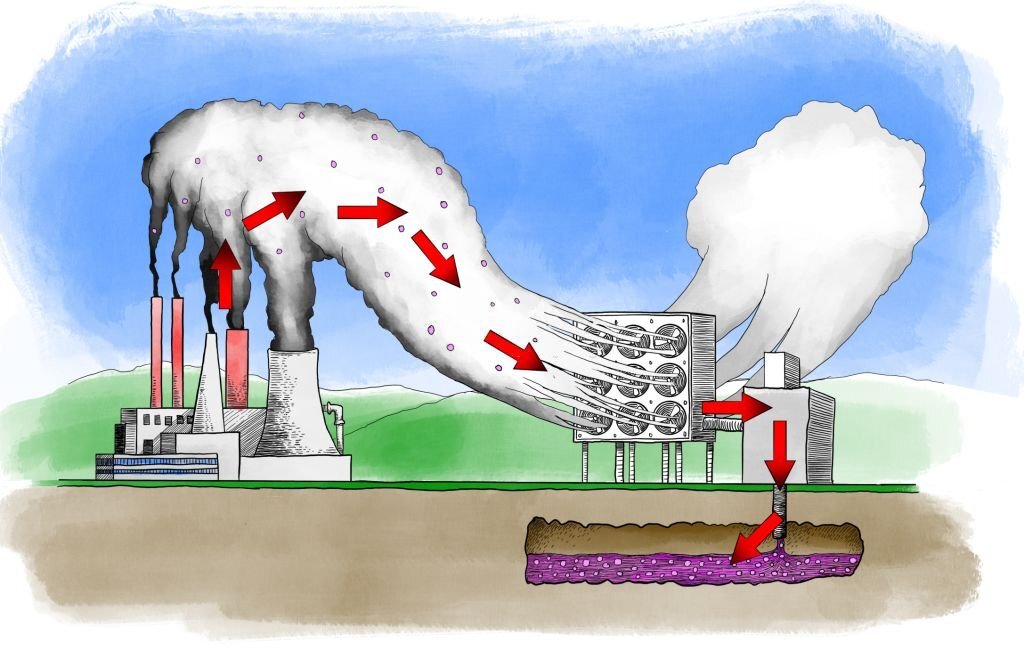
Carbon capture technology is a complex process that involves three distinct stages:
- Capture: The first step involves separating CO2 from other gases produced at power plants or during industrial processes. There are three primary methods of capture: post-combustion, pre-combustion, and oxyfuel combustion. Each method has its unique advantages and challenges, and the choice of method depends on the specific circumstances and requirements.
- Transport: Once the CO2 is captured and compressed, it needs to be transported to a storage site. This is typically done through pipelines, although other methods such as shipping can also be used for longer distances or when the terrain is challenging.
- Storage: The final step involves storing the captured CO2 underground in geological formations. These can include depleted oil and gas fields or deep saline aquifers. The CO2 is injected into these formations, where it is stored safely and permanently.
The Potential of Carbon Capture
The potential impact of carbon capture technology on our environment is enormous.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies have the potential to capture up to 90% of CO2 emissions from power plants and industrial facilities.
This represents a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, which is crucial in our fight against climate change.
But the benefits of carbon capture technology extend beyond just reducing emissions. The captured CO2 can also be utilized in a variety of ways.
For instance, it can be used to enhance oil recovery, produce fuels and chemicals, or even in the food and beverage industry. This not only helps to further reduce CO2 emissions but also creates economic opportunities and jobs.
Challenges and the Path Forward
Despite its immense potential, carbon capture technology is not without its challenges. One of the main hurdles is the high cost associated with capturing, transporting, and storing CO2.
Additionally, the process of capturing CO2 is energy-intensive, which can further increase costs and potentially offset some of the environmental benefits.
Another challenge is the need for extensive infrastructure for transporting and storing CO2. Building this infrastructure can be a complex and time-consuming process, involving numerous regulatory and logistical hurdles.
However, these challenges are not insurmountable. Researchers around the world are working tirelessly to develop new materials and processes that can make CO2 capture more efficient and cost-effective.
Moreover, there is growing interest in carbon capture and utilization (CCU), which aims to convert captured CO2 into valuable products.
This not only provides a potential revenue stream but also helps to create a circular economy where CO2 is not just a waste product but a valuable resource.
The Role of Carbon Capture in the Energy Sector
The energy sector, being one of the largest contributors to global CO2 emissions, stands to benefit significantly from carbon capture technology.
Power plants and industrial facilities that burn fossil fuels for energy are prime candidates for carbon capture systems.
For instance, post-combustion capture, which involves capturing CO2 after fossil fuels have been burned, can be retrofitted to existing power plants.
This makes it a potentially attractive option for reducing emissions from the existing energy infrastructure.
On the other hand, pre-combustion capture, which involves capturing CO2 before the fossil fuels are burned, could be particularly useful for new power plants.
This method typically results in a higher concentration of CO2, which can be easier and more cost-effective to capture.
Carbon Capture and the Environment
Beyond its potential for mitigating climate change, carbon capture technology also has significant implications for the environment.
By reducing CO2 emissions, carbon capture can help to slow the rate of global warming, potentially mitigating some of the most harmful effects of climate change.
Moreover, by storing CO2 underground, carbon capture technology can help to reduce the amount of CO2 that ends up in the atmosphere, where it can contribute to air pollution and other environmental problems.
The Economic Potential of Carbon Capture
While the environmental benefits of carbon capture are clear, this technology also holds significant economic potential.
The process of capturing, transporting, and storing CO2 requires a wide range of technologies and services, potentially leading to the creation of new industries and jobs.
Moreover, the utilization of captured CO2 can create additional economic opportunities. For instance, captured CO2 can be used to enhance oil recovery, potentially increasing the profitability of oil extraction operations.
In addition, the conversion of captured CO2 into fuels, chemicals, and other valuable products can create new revenue streams, further increasing the economic attractiveness of carbon capture technology.
The Future of Carbon Capture
Looking ahead, the future of carbon capture technology appears promising. As the world continues to grapple with the challenge of climate change, the demand for effective solutions like carbon capture is only expected to grow.
However, realizing the full potential of carbon capture technology will require continued research and development, as well as supportive policies and regulations.
With the right combination of innovation and policy support, carbon capture technology could play a crucial role in our transition to a sustainable, low-carbon future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, carbon capture technology represents a significant step forward in our fight against climate change.
While there are challenges to overcome, the potential benefits of this technology are too great to ignore.
With continued research and development, and the right policy support, carbon capture technology could play a crucial role in our transition to a sustainable, low-carbon future.




